How to Optimize Fluid Control with a 3 Way Valve in Your System
In modern fluid control systems, the selection and optimization of components play a critical role in enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs. A pivotal component in this domain is the 3 way valve, which offers versatile flow management solutions by allowing fluid to flow in multiple directions, thus facilitating complex processes in various industries, from petrochemicals to water treatment. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global valve market is projected to reach USD 80 billion by 2026, spurred by advancements in automation and increased demand for efficient fluid control systems. Optimizing the use of a 3 way valve not only improves system performance but also contributes to energy savings, with potential reductions in energy consumption by up to 30%. This article will explore key strategies to effectively integrate and optimize 3 way valves in your fluid control systems, ensuring optimal flow paths and improved system reliability.

Understanding the Basics of 3 Way Valves and Their Functionality
Three-way valves play a crucial role in fluid control systems by enabling efficient redirecting of flow paths. They are designed with three ports: one inlet and two outlets, or vice versa. This functionality allows them to either mix fluids from different sources or distribute a single fluid to multiple destinations. The unique design of three-way valves facilitates various operations, such as switching between heating and cooling systems or balancing fluid distribution in complex networks.
Understanding their operation requires recognizing the two main types of three-way valves: the mixing valve and the diverting valve. A mixing valve combines two inflows, adjusting the temperature or concentration based on the desired output. In contrast, a diverting valve directs a single inflow to one of two possible outlets, which is essential for processes that depend on precise flow management. By utilizing three-way valves effectively, engineers can enhance system efficiency, improve response times, and maintain optimal control over fluid dynamics.
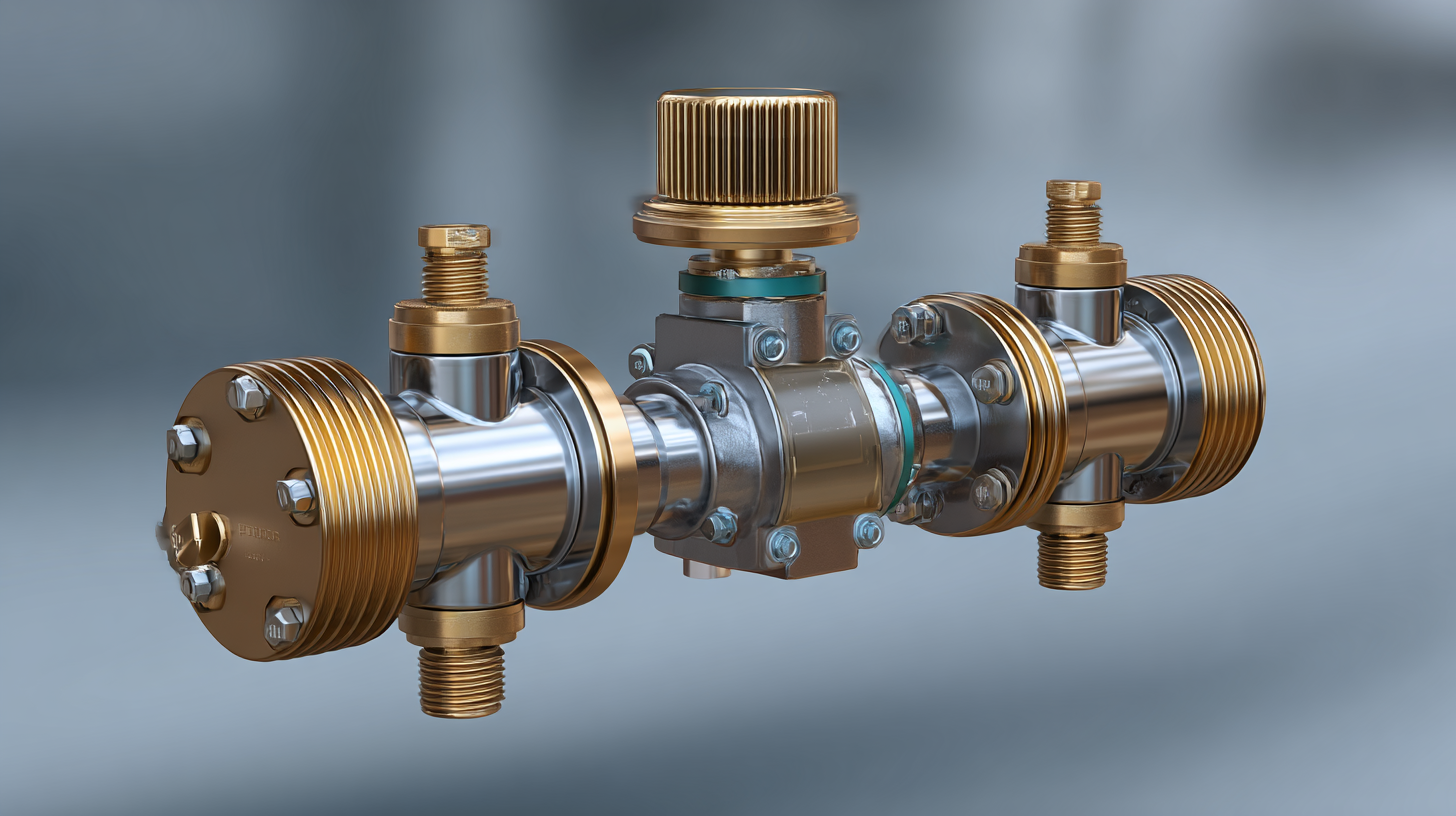
Identifying the Right Type of 3 Way Valve for Your Fluid System
When selecting a 3-way valve for your fluid system, it is crucial to consider the specific needs of your application. There are several types of 3-way valves, including L-port and T-port configurations. L-port valves are ideal for diverting flow between two different paths, making them suitable for applications where you need to control the direction of the fluid effectively. On the other hand, T-port valves are designed to combine or split fluid flows, thus providing greater versatility in managing multiple fluid streams within a system.
In addition to the configuration, the material of the valve is another key factor to consider. Depending on the fluid type—be it water, oil, or chemicals—you may need a valve made from brass, stainless steel, or plastic. Each material offers different levels of corrosion resistance, pressure tolerance, and temperature limits. Evaluating these factors against your fluid characteristics will ensure that you choose a 3-way valve that not only fits your operational needs but also enhances the overall efficiency and reliability of your fluid control system.
Key Techniques for Installing 3 Way Valves Effectively
When it comes to installing 3-way valves, a few key techniques can enhance the overall effectiveness of fluid control in your system. First, it's crucial to select the right type of valve for your application, whether it's a T-shape or L-shape configuration. Understanding the flow direction and how it interacts within your specific process can help you make an informed choice. Additionally, ensuring that the valve is compatible with the fluid medium and operational pressures is essential for optimal functionality.

Another important aspect is the proper mounting and alignment of the valve. Ensuring a level installation can prevent strain on the valve body and connections, which can lead to leaks or mechanical failure. It's also wise to install the valve in a location that allows for easy access for maintenance. Lastly, utilizing high-quality seals and fittings can ensure a tight, leak-free connection, which is vital for maintaining system efficiency and safety. Following these techniques will optimize the performance of 3-way valves and contribute to more reliable fluid control in your system.
Improving Efficiency: Tips for Maintaining Your 3 Way Valve
Maintaining the efficiency of a 3-way valve is crucial for optimizing fluid control in industrial systems. Regular maintenance practices can significantly enhance the lifespan and performance of these valves. According to a report by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, proper maintenance can reduce operational failures by up to 30%, which saves companies considerable repair costs and downtime. Essential maintenance tasks include regular inspections to check for leaks, wear, and valve alignment, which should be part of a scheduled preventive maintenance plan.
Moreover, lubrication is key to ensuring smooth operation and minimizing friction in the valve mechanism. The International Society of Automation suggests that using the correct type of lubricant can improve valve efficiency by up to 15%. Additionally, monitoring the actuator response time helps ensure the valve reacts properly to system demands, and any delays can indicate maintenance needs. By implementing these tips, industries can not only enhance the operation of their 3-way valves but also improve overall system effectiveness and reliability.
Common Issues with 3 Way Valves and How to Troubleshoot Them
Three-way valves play a crucial role in fluid control systems, but they can encounter several common issues that may affect their performance. One frequent problem is leakage, which can occur due to improper installation or wear and tear of the seals. It is essential to regularly inspect the valve for signs of leakage and ensure that it is correctly tightened to prevent fluid loss.
Another common issue is valve sticking, which often arises from sediment buildup or lack of lubrication. To troubleshoot this, operators should perform routine maintenance by cleaning the valve internals and applying appropriate lubricants to the moving parts. Additionally, ensuring that the fluid flowing through the system is free of excessive particulate can help mitigate sticking problems.
**Tips:** Always ensure you choose the right valve material for your specific application to minimize wear. Regular maintenance checks, including cleaning and inspection, can extend the life of your valves. When replacing a valve, verify compatibility with existing system pressure and flow requirements to avoid future malfunctions.
Fluid Control Optimization with 3 Way Valves
This chart illustrates the key performance metrics for optimizing fluid control using 3 way valves. The values represent the flow rate, pressure drop, and valve response time, which are critical for assessing the efficiency and functionality of 3 way valves in systems.
Related Posts
-

5 Reasons Why the Best 3 Flanged Ball Valves Revolutionize Industrial Efficiency
-

Solutions for Choosing the Best Steel Ball Valves: Key Insights from Industry Trends and Data
-

7 Unique Benefits of Metal Seated Ball Valves for Global Procurement Success
-

Complete Guide to Choosing the Right Full Port Ball Valve for Your Project
-

Advantages of 3 Flanged Ball Valves for Efficient Fluid Control Solutions
-

Comparing Three Way Valve Designs for Optimal Efficiency in Global Supply Chains
